4. Control Real Robotusing AI
This section describes how to run an AI policy to control the robot after data has been collected and a model has been trained. The provided tools support policy validation, testing, and runtime parameter adjustments.
Required Equipment
- Laptop with a NVIDIA graphics card
- RealMan RM65 robotic arm
Configuration
Use the same configuration as described in section 3. For details on setting up the inference pipeline, refer to the Policy Execution section in hrc-dexman/README.md.
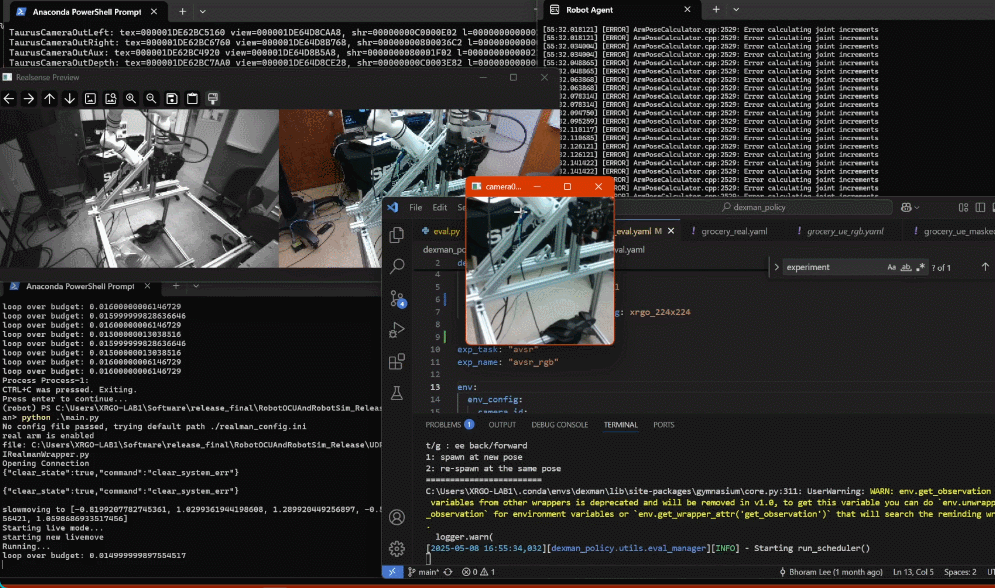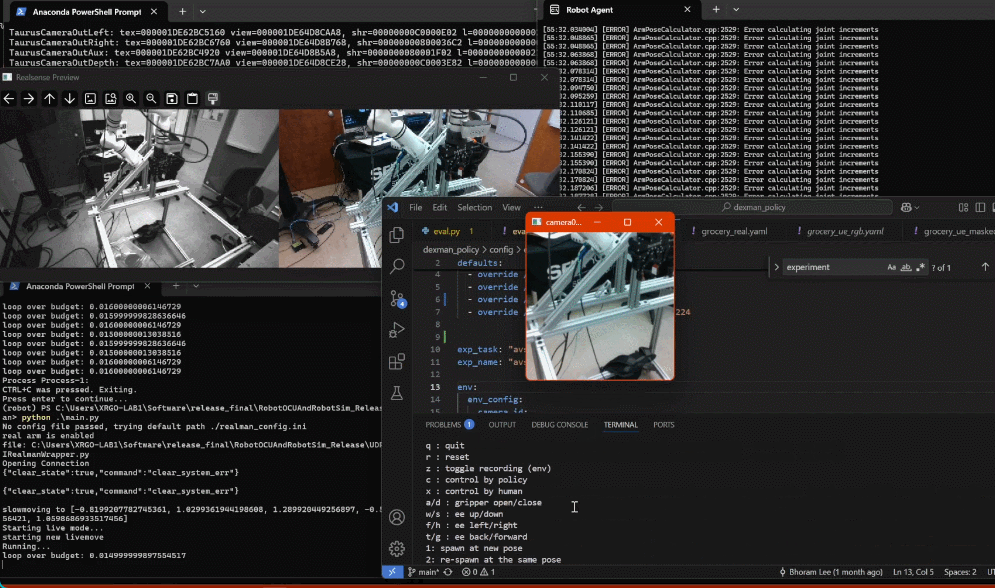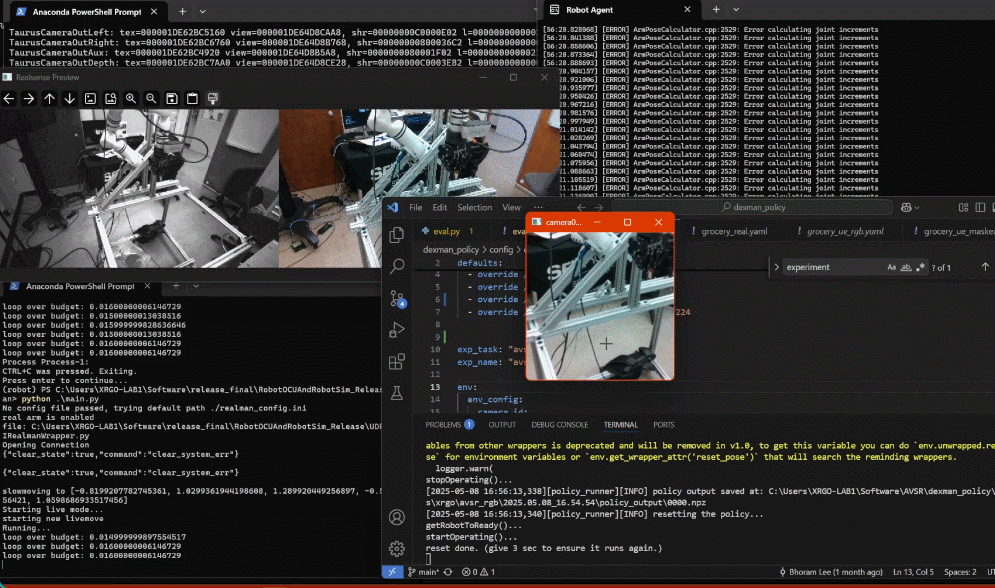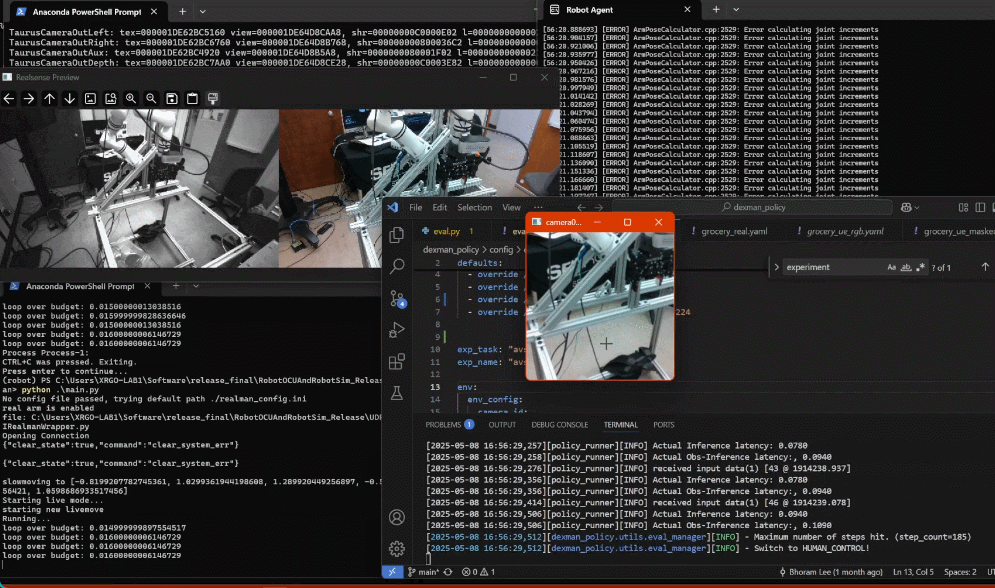
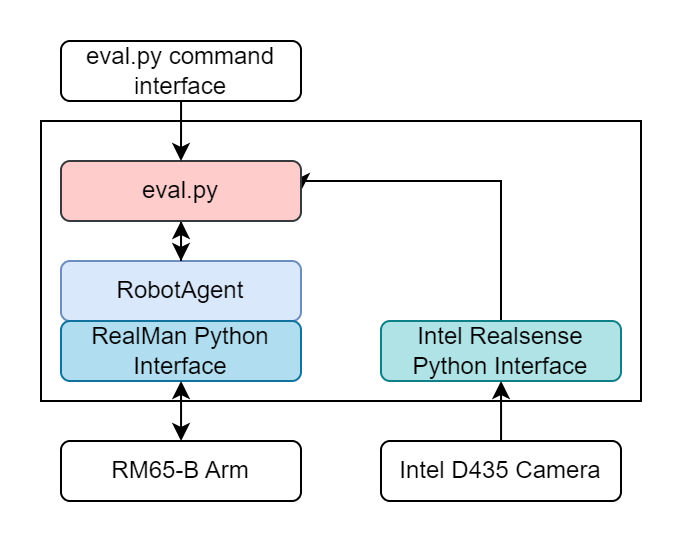
Running the System
Run the RealSense wrapper. Using the
dexmanConda environment, start the python scriptSuperDex_interface\apps\realsense_SuperDex\realsense_to_sui.py. The camera should load and ifpreview=Truein the config file, you should see the data streaming in.Power on the arm. The arm takes roughly 45-60 seconds to fully power on, even after the relays click on and energize the motors. The full web server at http://192.168.1.18 must be running to interface.
Run the RealMan wrapper. This requires setup found in
RobotOCUAndRobotSim_Release\UDPRobotControlPython\README.mdfor the Conda environment. Then, you cancdinto the source directory and runRobotOCUAndRobotSim_Release\UDPRobotControlPython\RealMan\main.py. The script will start up and be in control of the arm.If using two arms, run two instances of the wrapper, each configured with the correct IP address.
Double-click
RobotOCUAndRobotSim_Release\Run RobotAgent.bat. RobotAgent will connect to the RealMan wrapper.Start
dexman_policy/eval.py. An OpenCV window will open, and a console window will print program status. Eventually, the console output will include a list of available keystrokes and what they do.Click on the OpenCV window to register keystrokes there, and monitor the output on the console window.